Information on how to use R Scripts and R Markdown files
On this page
Video setup guide
Note that this video demonstrates how to use scripts in R. If you are interested in using R Markdown see Section 4. This video assumes you already have RStudio installed and open.
We are using command/control + enter to run the code in this video.
Video guide showing how to get setup for R workshop
The following sections give more information on R scripts and R Markdown documents, as well as setup instructions for the workshops.
Opening RStudio
If you have not done so already, open RStudio!
Windows users
- Type
RStudioin the search bar (bottom left, next to windows symbol) - If you prefer, open the start menu (click windows symbol), then scroll until you find RStudio
Mac users
- Hit command + space and type in
RStudio - If you prefer to look for RStudio in an applications folder (open finder and select Applications on the left panel), you should be looking for this icon:

RStudio overview
When RStudio opens you should see a layout with 3 panels, similar to the image below.
The largest panel on the left with the > is the console. On the bottom right there is the files/plot panel, and top right is the environment panel.
If your installation of R and RStudio has worked, first RStudio should be open, and second you should see a message in your console panel telling you the version of R you have installed, like the image below.
There are three ways of running R code: the console, R scripts and R Markdown. In the R workshops we use R scripts, but R markdown can also be used if preferred.
R Scripts
An R Script file is a text file that contains a set of commands, or code, written in the R programming language. They are simple to use, allowing you to save the code you have written for later.
An in-depth description can be found in the R for Data Science open source book.
Opening R Scripts
If you move your mouse/courser to the top of your screen you will see a banner with file, edit, code etc.
To start a new R script: go to File > New File > R Script, or use the keyboard shortcut ctrl/command + shift + N.
To open a saved R script: use File > Open File..., find the R script file to load. R script files have the extension .R.
Using R Scripts
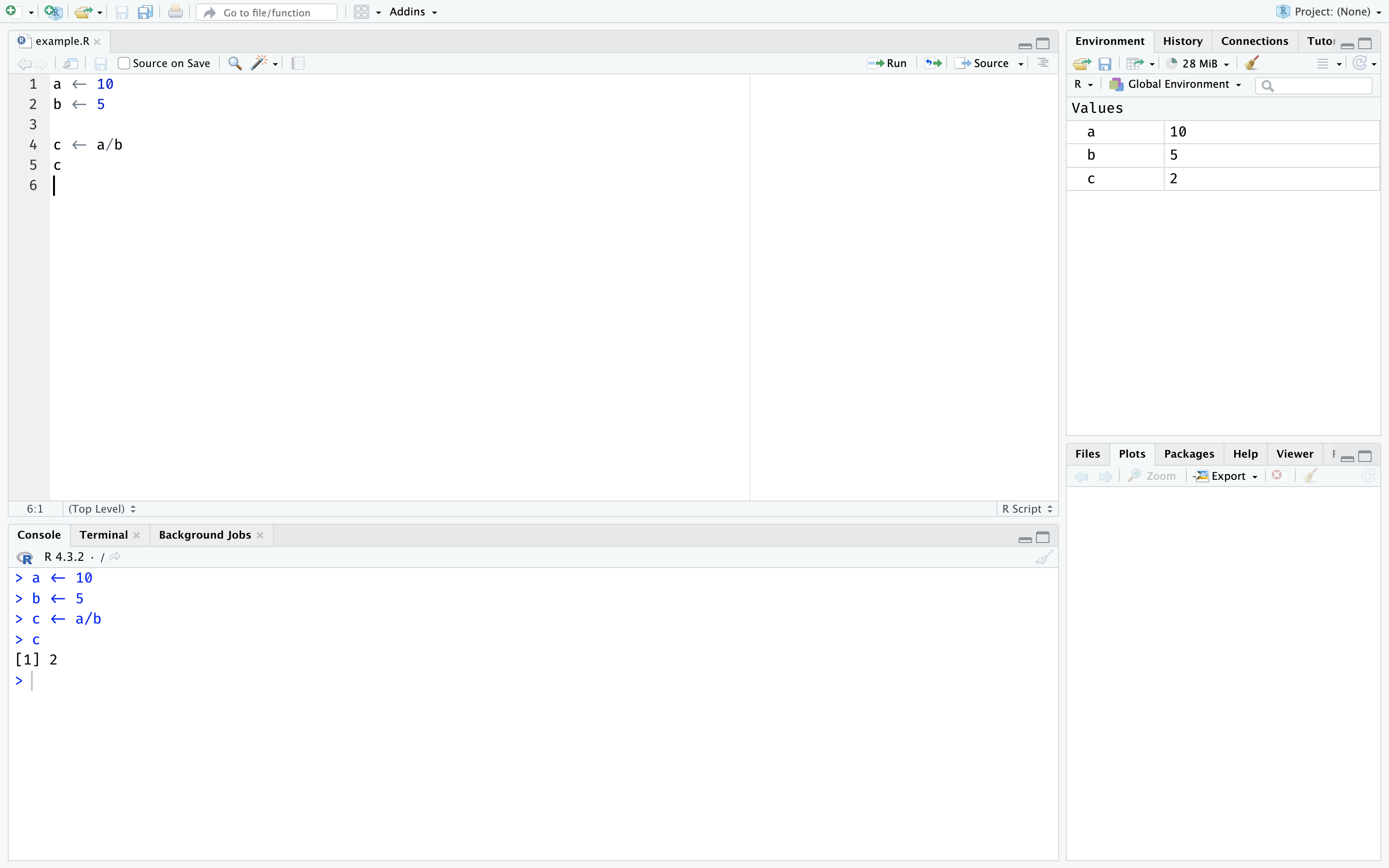
The below image shows an R Script in action.
There are two main ways of running code in an R Script.
- Use
ctrl/command + Enterto run each line - Highlight a section of code, and use the run button (or press
ctrl/command + Enter)
You might notice code you have run appears on the console (bottom left), and if you make a variable that will appear in the Environment (top right).
R Markdown
An R Markdown file has sections of text and code together in a single document. This is helpful for tutorials, documentation, and writing reports.
An in-depth description can be found in the R for Data Science open source book
Opening R Markdown files
Opening a R Markdown file is very similar to opening a file in other software. If you move your mouse/courser to the top of your screen you will see a banner with file, edit, code etc.
To start a new R markdown file: go to File > New File > R Markdown....
To load a R markdown file: Use File > Open File..., find the R Markdown file to load. R Markdown files have the extension .Rmd.
Using a R Markdown file
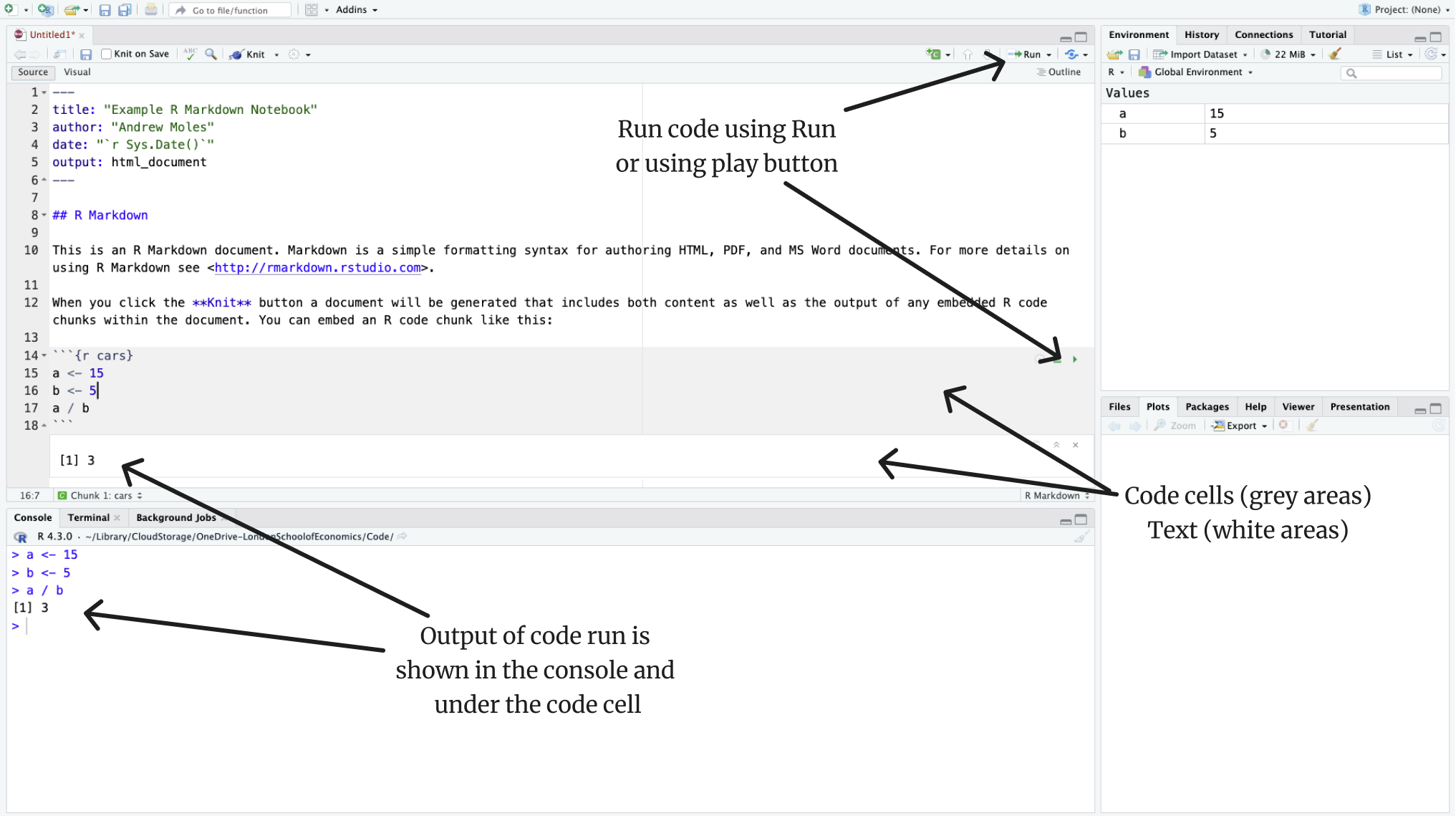
The image below shows the basic layout of a R Markdown document.
The top section (between the —) is the YAML header which is used when making documents from R markdown.
The hash tags show headers, and below them is text.
The grey sections are where you write your code.
There are three ways to run code in a code cell. The two ways mentioned in the image (Run and play button), and third is to use ctrl/command + Enter to run each line just like you would with an R script.
The most important thing for you to take note of is the code cells. Each code cell is like a small R script. You’ll notice the ``` markings around the code cell. It is important these do not get deleted, so be careful when editing your code!
A top tip is to change the mode of your R Markdown file from source to visual which provides a more pleasing environment to code in. To do this you will find the option near the top right of your RStudio window.
Finally, you can add your own code cell using option+command+i on a Mac or ctrl + alt + i on a Windows machine.
If you have struggled with any of these steps ask a trainer for support